What Drink can Cause Appendicitis?

Are you looking for what drink can cause appendicitis? sure, you have ever heard of appendicitis. It’s a medical condition that can happen to anyone, where the appendix becomes inflamed and can cause a lot of pain and discomfort.
It’s essential to seek immediate medical attention if you suspect you may have appendicitis, as it can become serious if left untreated. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the appendix.
It’s interesting to note that there is ongoing debate about the role of beverages in the development of appendicitis. Let’s make sure to stay informed about what drink can cause appendicitis.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Appendicitis
- What Drink can Cause Appendicitis
- Can soda cause Appendicitis
- Can Drinking cause Appendix pain
- Can I Drink milk with Appendicitis
Understanding Appendicitis
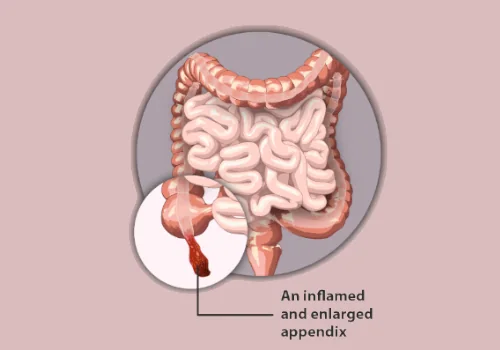
Before getting into the possible link between drink and appendicitis, it’s essential to understand the fundamentals of this condition. Appendicitis often causes abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
The specific cause of appendicitis is unknown, but it is frequently associated with an appendix blockage, which causes bacterial proliferation and inflammation.
What Drink can Cause Appendicitis
While there is no direct evidence connecting certain drinks to the development of appendicitis, various beverage-related factors may indirectly raise the risk. Here, we have listed what drinks make appendicitis worse.
1. Alcohol
Excessive alcohol drinking may irritate the digestive tract. While there is no direct evidence that alcohol causes appendicitis, chronic intestinal irritation may contribute to inflammation and other digestive problems.
2. Carbonated Drinks
I know we all love our soda fixes, especially during the hot summer months. But did you know that the carbonation in these drinks can irritate the lining of our digestive system, including our appendix?
Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal irritation or discomfort after consuming carbonated drinks. While this doesn’t directly cause appendicitis, chronic irritation of the gastrointestinal tract could theoretically contribute to inflammation over time.
3. High-Sugar Beverages
Consuming high-sugar beverages can lead to health issues like obesity and metabolic diseases. Obesity has been established as a risk factor for appendicitis. Therefore, these factors may have an indirect impact on its development.
4. Lack of Fiber
A low-fibre diet can cause constipation and have an adverse effect on gut health. Some beverages, particularly those with little nutritional value, might contribute to a fiber-deficient diet. This, in turn, may raise the risk of appendicitis.
5. Dehydration
I just learned something pretty interesting and important that I wanted to share with you all. Did you know that dehydration can actually lead to constipation and increase the risk of developing a fecalith?
That’s a hardened piece of stool that can block the opening of the appendix. It’s crazy to think that something as simple as not drinking enough water can have such a serious impact on our health.
And to make matters worse, drinking diuretic beverages like coffee and alcohol can worsen chronic dehydration.
Can soda cause Appendicitis?
Soda did not directly cause appendicitis. However, drinking too much soda can lead to dehydration, poor dietary habits, and even obesity. These factors, although not proven causes, have been linked to digestive health issues such as appendicitis.
Can Drinking cause Appendix pain?
Yes, excessive drinking can contribute to appendix pain and other various gastrointestinal issues, such as gastritis or pancreatitis, which may cause abdominal discomfort.
Can I Drink milk with Appendicitis?
When experiencing appendicitis symptoms, it is generally recommended to avoid dairy products, particularly milk, as they may increase intestinal discomfort.
Symptoms of appendicitis include stomach pain, nausea, and vomiting. Dairy products can be difficult to digest for some people and may cause additional gastrointestinal irritation.
Conclusion
While there is not sufficient evidence that certain drinks cause appendicitis, it is essential to consider the overall impact of beverage choices on health.
Maintaining a well-balanced diet, staying hydrated with water, and avoiding excessive consumption of sugary or alcoholic beverages can all help to promote a healthy digestive tract and may indirectly minimize the risk of appendicitis.
References
- What Is the Cause of Appendicitis (PDF)
- Acute Appendicitis -Jama
- Seasonal Variation in Cases of Acute Appendicitis