What to Expect the First week After Hip Replacement Surgery
Looking for what to expect the first week after hip replacement surgery. Congratulations on taking the first step towards a pain-free life! Hip replacement surgery is a remarkable procedure that can significantly improve your quality of life.
As you embark on this journey, it’s natural to have questions and concerns about what lies ahead. In this article, we’ll guide you through the first week after hip replacement surgery, providing you with valuable insights and helpful tips to help you navigate this crucial period.
In This Article
What to Expect the First week After Hip Replacement Surgery
Here we have described what to Expect the first week after hip replacement surgery
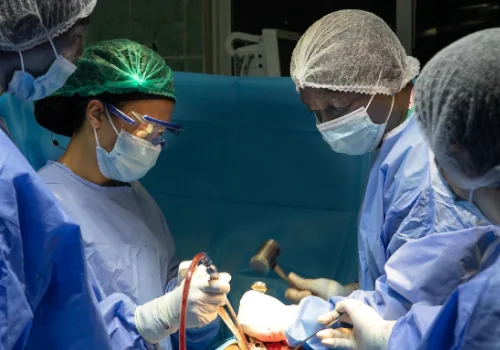
1. Recovery in the Hospital
Immediately after your surgery, you’ll spend some time in the hospital to ensure a smooth recovery. Expect to be closely monitored by a team of healthcare professionals who will ensure your pain is managed effectively and that you’re on the right track to recovery.
During this time, you’ll be encouraged to start gentle exercises and movement under the guidance of your healthcare team.
2. Mobility and Rehabilitation
Once you’re discharged from the hospital, your recovery will continue at home. Mobility and rehabilitation exercises will become an essential part of your daily routine.
Your surgeon or physical therapist will provide you with a tailored exercise program to improve your strength, flexibility, and overall mobility. Remember, patience is key during this stage as you gradually regain your independence.
3. Pain Management
Pain is an everyday companion during the initial phase of recovery. However, your healthcare team will work with you to manage it effectively.
They may prescribe pain medications or recommend non-pharmaceutical interventions like ice packs or heat therapy. Following their instructions diligently will help minimize discomfort and promote healing.
4. Support System
During the first week, having a strong support system is crucial. Enlist the help of family and friends to assist you with daily activities such as meal preparation, house chores, and transportation.
Their support will not only ease your load but also provide emotional encouragement throughout your recovery journey.
5. Rest and Sleep
Rest is vital for your body to heal and recover. Make sure to prioritize ample sleep and rest during the first week. Create a comfortable environment in your bedroom, use pillows to support your hip, and consider using aids like a raised toilet seat or shower chair to reduce strain. Remember to listen to your body and take breaks when needed.
6. Wound Care and Medications
Proper wound care and adherence to medication schedules are essential for a successful recovery. Follow your surgeon’s instructions on how to care for your surgical incision, including cleaning, dressing changes, and monitoring for signs of infection.
It’s essential to take prescribed medications as directed to manage pain, prevent complications, and promote healing.
7. Lifestyle Modifications
As you recover, certain lifestyle modifications may be necessary. Your healthcare team may guide weight management, dietary changes, and improvements to activities that could strain your new hip. Embrace these changes as they will contribute to your long-term success and overall well-being.
Conclusion
The first week after hip replacement surgery is a crucial period in your journey towards a pain-free life. By knowing what to expect and proactively preparing, you can ease your transition into recovery.
Embrace the support of your healthcare team, family, and friends, and remember to be patient with yourself. With time, dedication, and a positive mindset, you’ll be well on your way to regaining your mobility and enjoying a life free from hip pain.





